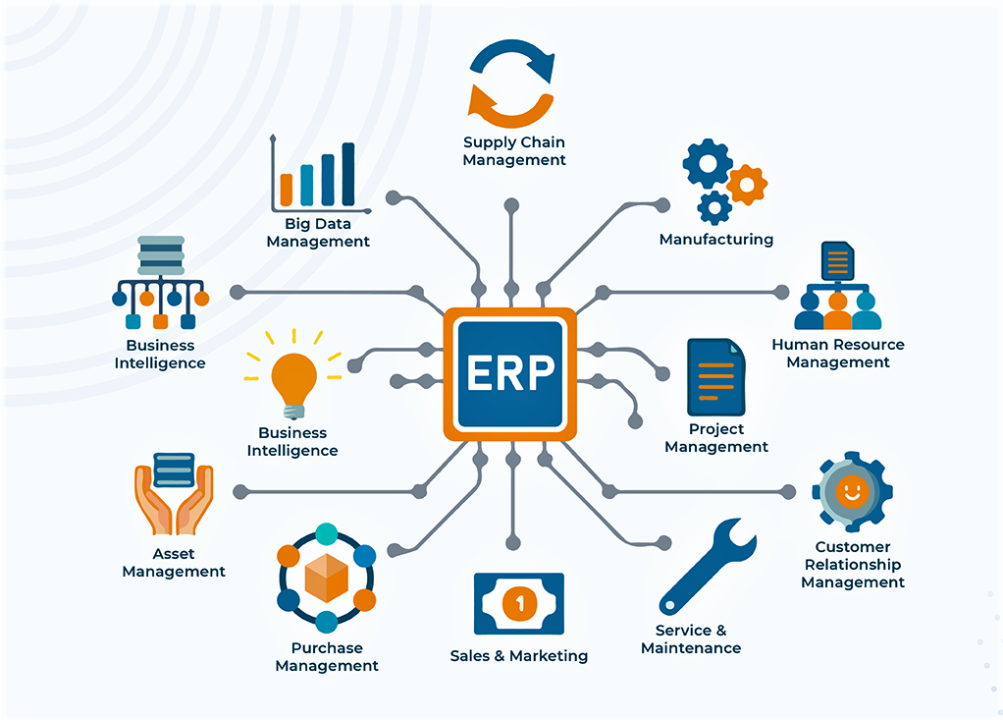
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are powerful tools that integrate various business processes into a unified platform, streamlining operations and improving efficiency across organizations. Each ERP system consists of several modules, each serving specific functions essential to different departments and functions within a company. Here’s a detailed exploration of common ERP modules and their functionalities:
1. Finance Module: Managing Financial Operations
The Finance Module in ERP systems is the backbone of financial management, encompassing a wide range of functions:
- Accounts Payable: Manages the company’s liabilities by tracking and processing payments to suppliers and vendors. It ensures timely payments while optimizing cash flow management.
- Accounts Receivable: Tracks and manages incoming payments from customers. It automates invoicing, monitors payment schedules, and improves cash flow forecasting.
- General Ledger: Acts as the central repository for financial data, consolidating all transactions from various modules. It provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s financial health through balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
- Financial Reporting: Generates detailed reports and analysis based on real-time financial data. It helps stakeholders, including executives and investors, make informed decisions by providing insights into profitability, liquidity, and financial performance.
2. Human Resources Module: Optimizing Workforce Management
The Human Resources (HR) Module in ERP systems is designed to streamline and enhance various aspects of workforce management:
- Employee Data Management: Centralizes employee information such as personal details, contact information, job roles, and historical data. It ensures data integrity and accessibility across the organization.
- Payroll Management: Automates payroll processes including salary calculation, tax deductions, benefits administration, and compliance with labor regulations. It ensures accuracy in payroll processing and timely payments to employees.
- Benefits Administration: Manages employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. It facilitates enrollment, updates, and compliance with benefit regulations, enhancing employee satisfaction and retention.
- Recruitment and Onboarding: Streamlines the recruitment process from job posting and candidate sourcing to interview scheduling and onboarding. It integrates with recruitment platforms and applicant tracking systems (ATS) to streamline hiring workflows.
- Training and Development: Tracks employee training needs, certifications, and skill development programs. It schedules training sessions, monitors progress, and evaluates training effectiveness to support employee growth and career development.
- Performance Evaluations: Facilitates performance reviews, goal setting, and feedback mechanisms. It supports continuous performance management practices, identifies top performers, and aligns individual goals with organizational objectives.
3. Manufacturing Module: Streamlining Production Processes
The Manufacturing Module in ERP systems is designed to optimize and streamline various aspects of production:
- Production Planning: Facilitates long-term and short-term production planning based on demand forecasts, resource availability, and capacity constraints. It aligns production schedules with customer orders and inventory levels.
- Scheduling: Automates the scheduling of production tasks, including machine operations, labor allocation, and job sequencing. It ensures efficient use of resources and minimizes downtime.
- Inventory Management: Manages raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods inventory levels. It tracks inventory movements, replenishment needs, and storage locations to prevent stockouts and overstock situations.
- Quality Control: Monitors and maintains product quality standards throughout the manufacturing process. It includes inspection protocols, quality assurance checks, and compliance with industry regulations.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Calculates material requirements based on production schedules and sales forecasts. It optimizes procurement processes, reduces excess inventory, and minimizes material waste.
4. Supply Chain Management (SCM) Module: Enhancing Logistics and Distribution
The SCM Module in ERP systems plays a crucial role in managing the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers:
- Procurement Management: Streamlines the procurement process, from supplier selection and RFQ (Request for Quotation) to purchase order creation and supplier relationship management. It ensures timely procurement of goods and services at optimal costs.
- Inventory Control: Manages inventory levels across multiple warehouses or locations. It tracks stock movements, monitors stock levels, and optimizes inventory replenishment to prevent stockouts and minimize carrying costs.
- Warehouse Management: Optimizes warehouse operations, including receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping goods. It improves warehouse efficiency, reduces order fulfillment times, and enhances inventory accuracy.
- Logistics Management: Coordinates transportation and distribution activities to ensure timely delivery of goods to customers. It optimizes route planning, freight management, and transportation costs to improve supply chain efficiency.
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): Strengthens relationships with suppliers through collaboration, performance monitoring, and contract management. It fosters strategic partnerships to secure reliable supply sources and negotiate favorable terms.

5. Sales and Marketing Module: Optimizing Customer Engagement
The Sales and Marketing Module in ERP systems focuses on driving sales growth and improving customer relationships:
- Sales Automation: Automates sales processes, including lead management, opportunity tracking, and quote generation. It streamlines sales operations and accelerates the sales cycle.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages customer interactions, tracks customer preferences, and maintains a centralized database of customer information. It enhances customer engagement and supports personalized marketing efforts.
- Campaign Management: Plans, executes, and tracks marketing campaigns across various channels. It measures campaign effectiveness, analyzes ROI (Return on Investment), and adjusts strategies to maximize marketing spend.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicts future sales based on historical data and market trends. It enables sales teams to set realistic targets, allocate resources effectively, and optimize sales strategies.
6. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module: Strengthening Customer Interactions
The CRM Module in ERP systems focuses on managing customer relationships and improving customer satisfaction:
- Sales Pipeline Management: Tracks sales opportunities through different stages of the sales funnel. It provides visibility into sales pipelines, forecasts revenue, and prioritizes sales efforts.
- Customer Service Management: Manages customer inquiries, complaints, and service requests. It ensures timely resolution of issues, improves service delivery, and enhances customer loyalty.
- Marketing Campaign Management: Plans, executes, and analyzes marketing campaigns to attract, engage, and retain customers. It integrates with sales data to measure campaign effectiveness and ROI.
- Customer Data Analysis: Analyzes customer data to identify trends, preferences, and buying behaviors. It supports targeted marketing initiatives, personalized customer communications, and predictive analytics.
7. Project Management Module: Coordinating Complex Projects
The Project Management Module in ERP systems facilitates effective planning, execution, and monitoring of projects:
- Project Planning: Defines project scope, objectives, timelines, and deliverables. It allocates resources, establishes dependencies, and creates project schedules to ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Resource Allocation: Assigns human resources, equipment, and materials to project tasks. It optimizes resource utilization, minimizes bottlenecks, and ensures efficient project execution.
- Task Management: Tracks task progress, milestones, and dependencies. It enables task prioritization, real-time updates, and collaboration among project teams for seamless project execution.
- Budgeting and Cost Management: Estimates project costs, creates budgets, and monitors expenditures against allocated funds. It tracks project expenses, identifies cost variances, and ensures adherence to budget constraints.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generates project performance reports, including Gantt charts, resource utilization dashboards, and project profitability analysis. It provides insights into project health, progress, and potential risks.
8. Inventory Management Module: Optimizing Inventory Levels
The Inventory Management Module in ERP systems ensures efficient handling and control of inventory across the supply chain:
- Inventory Tracking: Monitors inventory levels, stock movements, and item locations in real-time. It provides visibility into stock availability and facilitates accurate demand forecasting.
- Warehouse Operations: Manages warehouse activities, including receiving, picking, packing, and shipping. It optimizes storage space utilization, minimizes handling costs, and improves order fulfillment efficiency.
- Demand Forecasting: Predicts future demand based on historical data, sales trends, and market analysis. It supports inventory planning, stock replenishment, and prevents stockouts or overstock situations.
- Supplier Management: Coordinates with suppliers for timely deliveries, quality assurance, and vendor performance evaluation. It fosters strategic partnerships and ensures reliable supply chain operations.
9. Quality Management Module: Ensuring Product and Service Quality
The Quality Management Module in ERP systems focuses on maintaining and improving product and service quality standards:
- Quality Assurance: Establishes quality control processes, standards, and procedures to meet regulatory requirements and customer expectations. It ensures consistency and compliance across all operations.
- Inspections and Audits: Conducts inspections, audits, and quality checks throughout the production process. It identifies non-conformances, initiates corrective actions, and prevents quality issues from reaching customers.
- Document Control: Manages documentation related to quality standards, procedures, and certifications. It ensures document accuracy, version control, and accessibility for audit purposes and regulatory compliance.
- Continuous Improvement: Implements continuous improvement initiatives, such as Six Sigma or Lean methodologies, to enhance product quality, reduce defects, and optimize production processes.
10. Reporting and Analytics Module: Driving Informed Decision-Making
The Reporting and Analytics Module in ERP systems provides insights into business performance and facilitates data-driven decision-making:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Reporting: Generates customizable reports, dashboards, and visualizations to analyze key business metrics, trends, and performance indicators. It enables stakeholders to monitor organizational health and identify growth opportunities.
- Predictive Analytics: Applies statistical algorithms and machine learning models to forecast future trends, customer behavior, and market dynamics. It supports proactive decision-making and strategic planning.
- Financial Analysis: Analyzes financial data, profitability ratios, and cost structures to optimize financial performance, budget allocation, and resource utilization. It facilitates financial planning, forecasting, and scenario analysis.
- Operational Analytics: Evaluates operational efficiency, productivity levels, and process performance across departments. It identifies inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for operational improvements.
Benefits of ERP Modules
- Integrated Information: ERP modules unify data from different departments, providing a holistic view of business operations.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation of processes reduces manual errors and accelerates workflow.
- Data Accuracy: Real-time data updates ensure accurate reporting and informed decision-making.
- Scalability: ERP modules scale with business growth, accommodating additional users and functionalities.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined operations and optimized resource allocation reduce operational costs.
Choosing the Right ERP Solution
When selecting an ERP system like those offered by Synergics Solutions, businesses should consider their industry-specific needs, scalability requirements, customization options, integration capabilities, and ongoing support services. A well-implemented ERP system aligns business processes, enhances operational efficiency, and drives sustainable growth in today’s competitive landscape.
For more information on ERP modules and how they can benefit your organization, contact Synergics Solutions today.